Introduction
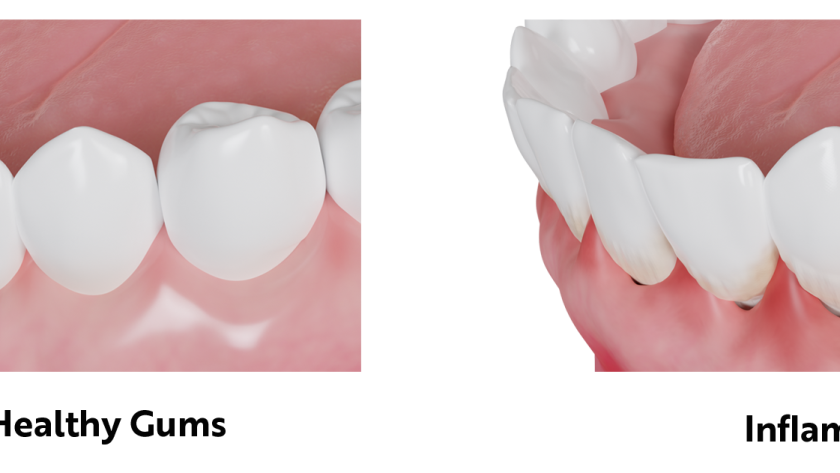
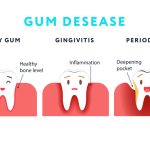
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, gum disease can progress and result in tooth loss and other serious complications. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available to manage and treat gum disease. In this article, we will explore the various gum disease treatments, from scaling to surgery.
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing, also known as deep cleaning, is a non-surgical treatment for gum disease. It involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the root surfaces to prevent bacteria from reattaching. This procedure is usually performed by a dental hygienist and may require multiple visits depending on the severity of the gum disease.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat gum disease. These medications can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas. Antibiotics help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection and reduce inflammation. They are often used in conjunction with other treatments to enhance their effectiveness.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a minimally invasive treatment option for gum disease. It involves using a dental laser to remove infected tissue and promote gum reattachment. Laser therapy is less painful and requires less downtime compared to traditional surgery. It also stimulates the growth of new, healthy gum tissue.
Gum Grafting
In advanced cases of gum disease where the gums have receded, gum grafting may be necessary. This surgical procedure involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth, such as the palate, and grafting it onto the affected areas. Gum grafting helps restore the gumline, protect the tooth roots, and improve the overall appearance of the smile.
Pocket Reduction Surgery
When gum disease progresses, deep pockets can form between the gums and teeth, allowing bacteria to thrive. Pocket reduction surgery, also known as flap surgery, aims to reduce the pocket depth and eliminate bacteria.
Summary
Gum disease treatments encompass a range of procedures aimed at combating the progression of periodontal disease and restoring oral health. The following are some common treatments:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This non-surgical procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and smoothing the root surfaces to prevent further bacterial growth.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
- Flap Surgery: For advanced gum disease, flap surgery may be necessary. It involves lifting the gums to remove tartar and bacteria, and then suturing them back in place.
- Bone and Tissue Grafts: In severe cases where bone or gum tissue has been lost, grafting procedures can help regenerate and restore the affected areas.
- Dental Implants: If tooth loss occurs due to gum disease, dental implants can be an effective solution for replacing missing teeth.
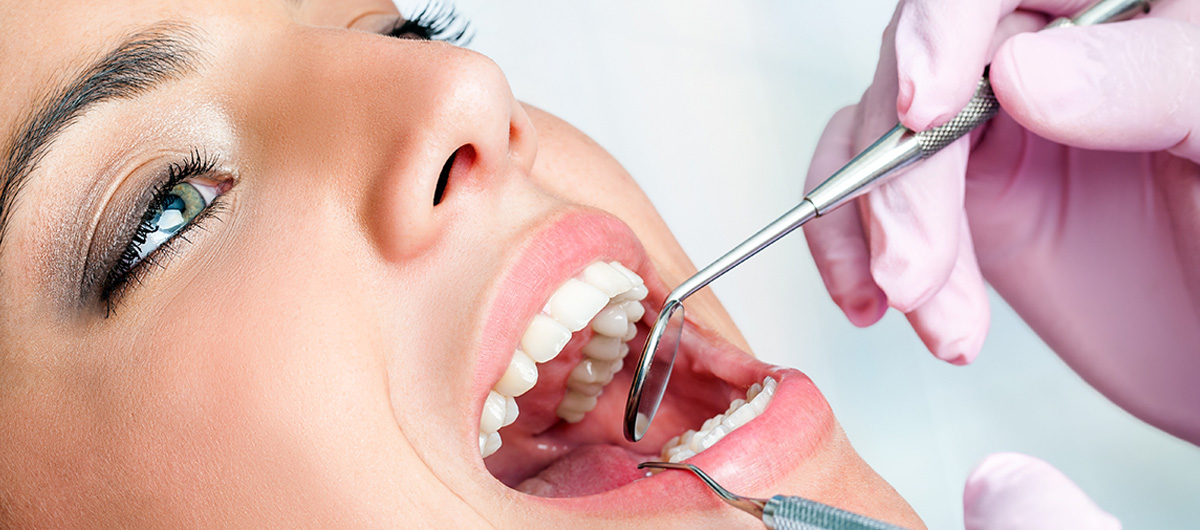
It is important to note that the specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of the gum disease and try this website individual patient needs. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene practices are crucial in preventing and managing gum disease.
- Q: What is gum disease?
- A: Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth.
- Q: What are the common symptoms of gum disease?
- A: Common symptoms of gum disease include swollen or tender gums, bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, receding gums, and loose teeth.
- Q: How is gum disease treated?
- A: Gum disease can be treated through various methods, including scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, gum graft surgery, and laser therapy.
- Q: What is scaling and root planing?
- A: Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar from the teeth and smoothing the root surfaces to promote gum tissue healing.
- Q: When is gum graft surgery necessary?
- A: Gum graft surgery may be necessary when the gums have receded significantly, exposing the tooth roots. It helps to cover the exposed roots and prevent further gum recession.
- Q: What is antibiotic therapy for gum disease?
- A: Antibiotic therapy involves the use of antibiotics, either in pill form or as a topical gel, to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation in the gums.
- Q: How does laser therapy help in treating gum disease?
- A: Laser therapy uses a dental laser to remove infected gum tissue and promote gum reattachment. It is a minimally invasive and effective treatment option.

Welcome to my website! My name is Joseph Smith, and I am a dedicated and experienced Periodontist specializing in Teeth Whitening, Gum Disease Treatment, Dental Crowns & Bridges, and Root Canal Therapy. With a passion for oral health and a commitment to providing exceptional care, I strive to help my patients achieve and maintain healthy, beautiful smiles.